To define obesity and being underweight, it is first necessary to know what the concept of “normal” is for the body. In normal-weight status, the energy taken from food and the amount of energy consumed by the body are almost equal and the body fat rate in men is between 8% and 15%; In women is between 15% and 22%.
Obesity and being underweight are statuses formed due to the imbalance between the amount of energy taken and the amount of energy burned in general. The reason for this imbalance may be malnutrition or different reasons such as disease, genetic predisposition, stress and lifestyle.

Like obesity, being underweight does not occur with a one-day energy imbalance. For being underweight or obese, there must be an energy imbalance routinely and the same lifestyle must be continued for a while.
Overfeeding at one meal or in a day can be compensated by eating less or doing more physical activity on other meals and days. Likewise, if there is more energy consumption than the energy taken during the day due to undernutrition or high effort, this situation can be compensated for on other days.
For example, Formula 1 racing drivers lose close to 2 kilograms during a race; However, since there are nutrition programs to regulate this situation, these individuals do not have to be underweight.
Determination of Weight Status
Although obesity and being underweight are relative concepts that vary from individual to individual in daily life, they can be measured according to some criteria. The most practical of these criteria is “body mass index” and “measurement of waist and hip circumference”.
1. Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body mass index is the ratio of an individual’s body weight to height and is used in individuals aged 19 and over. An individual can calculate his own body mass index with the following formula;
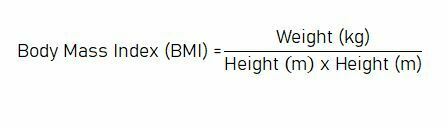
To give an example; The BMI of an individual weighing 80 kg and a length of 1.75 m;
= 80 / (1.75 x 1.75)
= 26.12
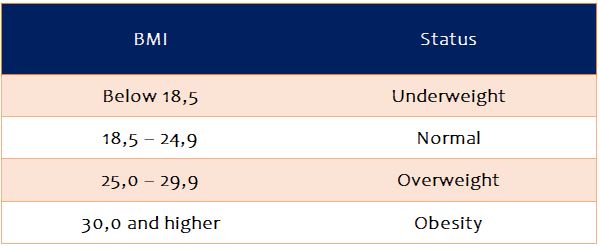
According to body mass index, weight status is defined in the table below. Accordingly, those with a BMI below 18.5 are underweight; Those between 25 and 30 are overweight; Those over 30 are classified as obese.
2. Evaluation According to Waist and Hip Circumference
The measurement of waist and hip circumferences is a very practical and useful method for measuring obesity and being underweight since they are the areas where fat is stored in the body.
A waist circumference of more than 94 cm in men is considered risky for health. A waist circumference of more than 102 cm poses a high health risk.
A waist circumference of more than 80 cm in women is considered risky for health. A waist circumference of more than 88 cm poses a high health risk.
Not only waist measurement but also the ratio of waist and hip measurement is frequently used as a risk indicator. For this purpose, waist circumference (cm) is divided by hip circumference (cm);
= Waist(cm) / Hip(cm)
This value should not exceed 0.8 for women and 1.0 for men. Having values higher than these is considered a risk factor for diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Being Overweight and Obesity
Being overweight and obese is a condition that occurs as a result of the energy get from food routinely more than the energy burned. Obesity can be defined as a higher form of being overweight.
The body stores unused energy as fat, thus increasing the amount of adipose tissue. The greater the difference between the energy get and the energy expended and the longer this lifestyle is maintained, the higher the degree of obesity.

It would not be a mistake if it were said that “obesity is the problem of our age”. The convenience that technology has provided to human life has inevitably brought the problem of being overweight and Obesity on a global scale.
Relatively easy food supply, the industrial revolution and the development of technology have had a double negative effect on Obesity by reducing the amount of physical activity that individuals have done as well as increasing food consumption.
Until roughly 70 years ago, people were generally engaged in farming; transportation was provided on foot or by horses and the work was usually based on muscle power. In nutrition, there was no fast food and sugary drinks that give high energy; It was a time when food supply was relatively difficult.
As a matter of fact, the energy taken with food could only be enough for the energy burned in daily work. Today, society’s way of life has changed radically and this change has seriously increased the obesity rate.
Worldwide, obesity has nearly tripled since 1975. In 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults aged 18 years and older were reported to be overweight. More than 650 million of these were reported as obese. These data show that 39% of the world’s population was overweight in 2016; which means that 13% are obese.
Risk Factors in Obesity
The following risk factors in an individual may cause obesity and a tendency to obesity. The coexistence of more than one of these risk factors can increase the effect. However, even if one or more of the risk factors is present, this does not mean that the individual will be obese in his destiny. Most risk factors can be neutralized through diet, physical activity, exercise and behavioral changes.
1. The influence of genetic inheritance and family
Genes from the family determine the amount of fat that the body will store and in which parts of the body this fat will be stored. However, gene inheritance also affects the efficiency of the energy produced from the consumed foods, the regulation of the appetite and the efficiency of the energy spent in physical activity. In this context, genetic inheritance can cause the body to be prone to obesity.
Another effect of the family is that it gives the individual the habit of eating. Therefore, individuals growing up in families with obese and obese parents are at risk of obesity due to both effects.
2. Lifestyle
It includes lifestyle, physical activities and nutrition programs. Individuals who work at desk jobs where physical activity is very low and individuals who routinely spend their days sedentary tend to gain weight.
In terms of nutrition;
- Not consuming enough vegetables and fruits,
- Excessive consumption of beverages such as high-energy alcohol and drinks containing high sugar that without give a feeling of satiety,
- Consuming foods high in fat on a routine basis
- Not consuming enough dietary fiber
- Not consuming enough fermented food,
- Consuming food cooked by frying method on a routine basis,
- Excessive consumption of fast food
- Individuals who routinely consume more than satiating are at risk of obesity.
3. Age
The tendency to gain weight can occur at any age. However, as it is known, the individual is more physically active during infancy, childhood, youth and the amount of physical activity decreases as one gets older.
Hormonal changes along with the decrease in physical activity increase the risk of obesity in older ages. However, as age progresses, the amount of muscle in the body tends to decrease.
The decrease in muscle tissue causes the basal metabolism to slow down and therefore the body’s energy needs decrease. If this situation is not taken into account in nutrition and the amount of food consumption is not reduced, weight gain may become inevitable.
4. Some diseases and drugs
Prader-Willi syndrome, Cushing’s syndrome and other diseases can cause obesity. Conditions such as arthritis can cause weight gain as they limit physical activity.
Some medications can also cause weight gain. Especially when some antidepressants, anti-seizure drugs, diabetes drugs, antipsychotic drugs, steroids and beta-blockers are used, weight gain may become inevitable if the weight gain effect of these drugs is not compensated through diet or physical activity.
5. Social and economic reasons
The social environment of the individual naturally affects the way of life. Similar eating habits and similar physical activities may cause individuals in the social environment to have similar weight statuses.
Therefore, if the individual’s social environment consists of obese and obese individuals, the individual is at risk of obesity. Similarly, if there is no safe social space for physical activities, this can lead to weight gain.
The individual’s purchasing power can affect the nutrition program. The inability to access healthy foods can be considered a risk factor for obesity.
6. Stress
Stress can cause different effects in different individuals. While some individuals lose weight during stress; In some individuals, it may cause the appetite to be more open and cause more food to be consumed. Changing eating habits during stress can be considered a risk factor.
7. Intestinal flora
Microorganisms living in the individual’s intestines are not only for the protection of the digestive system health; It is also extremely important for general health. Probiotic bacteria living in the intestines can prevent the individual from gaining excess weight. In this context, individuals with impaired intestinal flora may be more prone to obesity and may have difficulty in losing weight.
8. Quitting smoking
Weight gain is common after quitting smoking. Here, the following should be noted; Quitting smoking has greater long-term benefits than continuing to smoke for fear of gaining weight. After quitting smoking, the nutrition program can be changed to prevent weight gain and help from dietitians and doctors can be sought.
9. Pregnancy
Perhaps the most lovable factor that is effective in gaining weight in pregnancy. After pregnancy, the body weight can be regulated with a suitable diet program, taking into account breastfeeding. Maintaining the usual nutrition program after pregnancy and continuing to gain weight in this way may be a risk factor for gaining weight.
10. Irregular sleep
Insufficient sleep and too much sleep can cause hormonal changes that increase appetite. Therefore, sleeping less or more than the ideal sleep time can be considered a risk factor for obesity and obesity.
Diseases That Obesity May Cause
Obese individuals are potentially more likely to experience some of the following serious health problems;
1. Heart diseases and stroke; Obesity increases the likelihood of having high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels, risk factors for heart disease and stroke.
2. Type 2 diabetes; Obesity can affect how the body uses insulin to control blood sugar levels. This increases the development of insulin resistance and the risk of diabetes.
3. Cancer; Obesity increases the risk of cancer of the uterus, cervix, ovary, breast, colon, rectum, esophagus, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, kidney and prostate.
4. Digestive problems; The likelihood of developing heartburn, gallbladder disease and liver problems increases with obesity.
5. Sleep apnea; Obese individuals are more likely to have sleep apnea, a serious health problem.
6. Osteoarthritis; Besides promoting inflammation in the body, obesity increases the stress placed on weight-bearing joints. These factors can lead to complications such as Osteoarthritis.
Apart from these disorders, the individual may encounter mental and social problems such as obesity-induced depression, embarrassment, exclusion and social isolation.
Treatment of Obesity
Obese individuals should first decide to lose weight. Being determined and mentally ready for this process is the first and most important step. Losing weight is a process. Therefore, losing excess weight in a short time should not be considered; “patience” is the keyword. Stopping eating and drinking completely for the sake of losing weight as soon as possible is not a healthy way and is definitely not recommended.
The individual must make changes that will change his lifestyle. If the individual has faulty eating habits such as those listed under the lifestyle heading, they should be abandoned as soon as possible. The individual should increase the amount of physical activity and exercise. In this way, the necessary sub-conditions for weight loss will be provided.
In the case of obesity, the individual should definitely lose weight under the control of a doctor and dietitian. The individual should not create a diet and program on his own; He should not take credit for any written and visual publication, including this article and should not prepare his program.
As a matter of fact, metabolism and conditions are unique to the individual and each individual has to be evaluated in their way. What is required for one individual may not be required for another?
Doctors and dietitians are the ones who will diagnose this condition and chart a course. In this context, it is the healthiest and most efficient way to comply with the program determined by the specialist, under the control of a doctor and dietitian.
When a car breaks down, just as the individual does not try to repair it himself, he applies to the competent service; also, in order to lose weight, doctors and dietitians who are qualified should be consulted.
Health, not from the car; is more important than anything else and the necessary sensitivity should be given to health. In this process, it is very important to acquire healthy habits and maintain these habits for life, to prevent weight gain again after reaching normal weight.
Being Underweight
Being underweight generally occurs when the amount of energy taken from food is insufficient for the energy burned. If the amount of energy needed daily cannot be obtained from the foods eaten taken; To eliminate the energy deficit, the body starts to provide energy by first breaking down the fat tissue and then the muscle tissue. This also causes weight loss.
However, it is not enough to explain being underweight as just an energy imbalance. Being underweight can occur for many different reasons.
Being underweight can often be seen if the individual does not get enough nutrients necessary to continue his life activities healthily. The situation that occurs as a result of not getting enough energy and nutrients is called “malnutrition”.
It is “moderate malnutrition” for an individual to weigh 25 – 40% less than the average weight they should be; 40-60% less weight is considered “severe malnutrition”.
However, it should not be forgotten that; the cause of being underweight may also be conditions such as frequent and long-lasting illness, infections, secretion and absorption disorders in the digestive system and intestinal parasites.
Depending on the degree, malnutrition has different symptoms in the body, such as weakening the immune system. Prolonged full hunger is defined as “marasmus” and can result in death. A person’s body weight less than 60% of the average body weight is defined as marasmus. A significant portion of infant and child deaths are caused by malnutrition and marasmus.
Another reason for weight loss in terms of nutrition is adequate nutrition but insufficient content. As it is known, water, carbohydrates, fat, protein, vitamins and minerals are the nutrients that should be taken. The individual has to take all of these nutrients in a balanced way. However, the type of diet for always the same foods can cause weight loss by preventing the intake of all nutrients.
Conditions such as depression and stress, which reduce appetite, are also important factors that cause weight loss. As a matter of fact, the desire for nutrition does not awaken and thus the individual is deprived of the nutrients he needs. Likewise, some drugs and components that suppress appetite can also cause weakness.
Risk Factors in Being Underweight
1. Family and genetic inheritance
Gene inheritance and the lifestyle of the family can naturally affect the body structure and lifestyle of the individual.
2. High basal metabolic rate
A high basal metabolic rate can cause an individual not to gain weight. These individuals usually do not gain much weight even when eating high-energy foods.
3. Physical activity
Individuals who work in demanding jobs and engage in high levels of physical activity, such as athletes or runners, can burn a significant amount of calories resulting in weight loss.
4. Illness
Some diseases can cause weight loss by causing constant nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Some conditions can also reduce an individual’s appetite. Cancer, diabetes, thyroid disorders and ulcerative colitis can cause weight loss. Also, mental illnesses such as depression, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and anorexia and bulimia can cause eating disorders and weight loss.
Treatment of Being Underweight
Just like in the treatment of obesity, the first and most important step in treating being underweight is to make a decision. If the individual cannot gain weight even though they think that they have an adequate and balanced diet, they should definitely undergo a doctor’s examination to diagnose the cause of this situation.
As a matter of fact, the reason for being underweight can be malnutrition as well as different causes such as metabolic problems, diseases and parasites.
As a result, the healthiest and most efficient way to gain weight is to act under the control of a doctor and dietitian. If being underweight is caused by a disease, it must be treated first. The individual should not create a nutrition program by taking credit for written and visual publications; must comply with the schedule of doctors and dietitians.
One of the biggest mistakes individuals make in gaining weight is consuming a large number of eggs as a cheap and high protein source. The egg is a very rich food and contains almost all nutrients in a balanced way.
However, one egg contains about 200 mg of cholesterol. Eating five eggs a day for the sake of gaining weight means taking about 1000 mg of cholesterol into the body. It is recommended that cholesterol intake should not exceed 300 mg per day. In this context, it is obvious that this wrong diet will invite severe cardiovascular diseases in the future.
Here is an article that might interest you;
Energy Metabolism – II: Energy Expended by the Body



Be First to Comment