Roles and Functions of Fats in the Body
1. Most lipids are the building blocks of the human body. (The concept of lipid is a broad concept that includes fats, oils, fatty acids, phospholipids and steroids.)
2. Fats are the body’s energy stores. Excess calories taken into the body are stored in the form of fat. Energy is provided by using stored fats for calorie needs.
3. Fats provide heat isolation and protect the body against cold.
4. The subcutaneous fat tissue protects the body against impacts, while the adipose tissue surrounding the organs protects the organs against sudden physical effects.
5. Eating healthy fats supports brain health. It found a strong association between healthy fat consumption and a lower risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
6. Vitamins A, D, E and K are fat-soluble. Therefore, fat must be consumed to take these vitamins into the body. Likewise, the transport of these vitamins in the body is provided by fats.
7. Since fats stay in the stomach longer than proteins and carbohydrates, they provide a feeling of satiety for a more extended period.
Fats and Nutrition
It is recommended that a healthy adult consume about 70 grams of fat daily. In this context, each individual should know the fat content of the foods they consume. If the amount of fat in the consumed prepared foods and cooked meals is known, breakfast fat consumption can also be calculated.
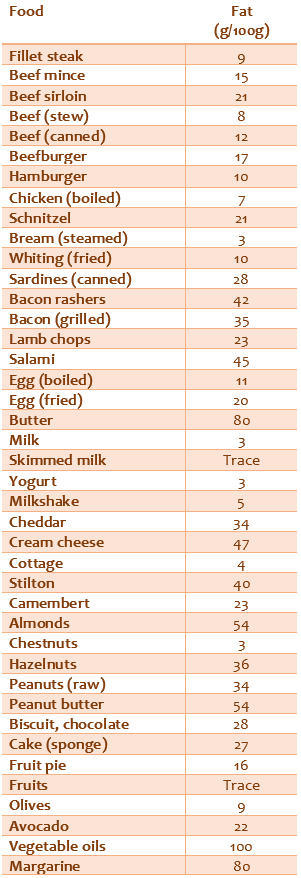
It is not a reasonable way to altogether remove fat from the diet in the problem of being overweight. Fat consumption is required to obtain fatty acids such as linoleic acid, linolenic acid and arachidonic acid; the human body cannot make them. From this point of view, it is preferable to consume foods rich in these fatty acids, such as fish and butter, rather than completely removing fat from the diet.
Fat consumption is also necessary for the intake of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. Although these vitamins can be stored in the body, if fat is not consumed for a long time, the body will be deprived of these vitamins.
On the other hand, foods produced by deep frying cause the individual to consume high-fat levels. Therefore, caution should be exercised in the consumption of such foods.
It has been suggested that erucic acid, one of the fatty acids, causes heart lubrication. Therefore, the consumption of rapeseed oil containing high erucic acid is not recommended.
Trans fatty acids are isomers of unsaturated fatty acids. Unsaturated fatty acids are usually present in foods in cis form. Fatty acids in trans form have a 25-30oC higher melting point than their isomers, cis forms and their solubility is lower than in the cis form. Trans fatty acids are usually formed during processing.
Importance of Cholesterol for Health and Nutrition
Another important issue in fat consumption is cholesterol intake. Cholesterol is a lipid found only in animal fats.
Cholesterol has very important vital functions in the body;
- It is responsible for the digestion of fats in the body,
- It participates in the structure of nerve cells; About 17% of the dry matter weight of brain tissue is cholesterol.
- It participates in the structure of the cell wall in other tissues.
Cholesterol is also produced in the human body. A healthy individual’s body makes 1 to 4 grams of cholesterol per day and there are constantly 10 to 12 grams of cholesterol in the blood. The total amount in the body of an adult individual is about 150 grams.
The lack of cholesterol in the body causes the inability to digest fats and the deterioration of the cell structure in the tissues, especially in the nervous tissue.
The negative effect of cholesterol on health is that it causes cardiovascular diseases. The melting point of cholesterol is 159oC. It is found in the blood bound to proteins. This is why LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) and HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) levels are detected in blood cholesterol measurement.
The cholesterol level in the blood is highly dependent on factors such as genetic predisposition, obesity and stress.
Over time, the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries causes severe disorders such as atherosclerosis, chest pain and heart attack. In this respect, high cholesterol intake does not show any immediate or daily symptoms; It shows signs of post-accumulation over the years.
Therefore, regularly and routinely measuring the cholesterol level in the blood is extremely important in preventing diseases that may be caused by cholesterol in the future.
Cholesterol Level in the Blood
For a healthy adult individual, the total cholesterol level in the blood is expected to be 200 mg/dL and below. A total cholesterol level of 200 – 239 mg/dL is accepted as a limit value. 240 mg/dL and above are considered high values.
The LDL level in the blood should be below 100 mg/dL.
LDL value in the range of 100 – 129 mg/dL is acceptable for individuals without health problems; however, this value range is a situation that should be considered especially in individuals with cardiovascular disease and in individuals at risk of discomfort (such as for overweight, stress and genetic predisposition).
The value range of 130 – 159 mg/dL is borderline high,
160 – 190 mg/dL high,
Values of 190 mg/dL and above are considered very high.
HDL levels should be kept high.
HDL values lower than 40 mg/dL are considered a significant risk factor for heart disease.
Values between 41 and 59 mg/dL are considered borderline low.
An HDL level of 60 mg/dL and above is the desired condition.
The acceptable total cholesterol level for children is below 170 mg/dL. Borderline high values for children between 170 and 190 mg/dL. A total cholesterol level of 200 mg/dL and above is quite high for a child. LDL levels in children should be below 110 mg/dL.
Cholesterol and Nutrition
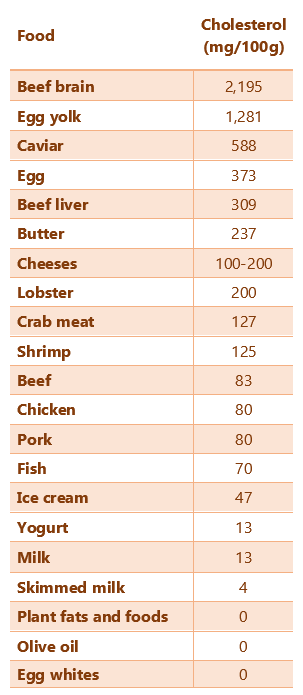
Cholesterol intake with food is recommended to be a maximum of 300 mg per day. As mentioned before, no plant food contains cholesterol. Foods that can be considered risky in terms of cholesterol are eggs and liver.
One hundred grams of beef is 83 mg; 1 egg is about 200 mg; 100 grams of beef liver contains about 300 mg of cholesterol.
Butter, which is stated to be careful in terms of cholesterol, has approximately 250 mg of cholesterol per 100 grams.
Considering that a daily individual consumes between 10-20 grams of butter, the cholesterol taken with butter is about 25-50 mg. However, only 50-60% of the cholesterol taken with food can be absorbed.
Finally, it is possible to say that cholesterol is an essential and important molecule for life; however, its high amount in the blood causes heart and vascular diseases. Blood cholesterol levels may be increased due to genetic predisposition, obesity, stress and high cholesterol intake in the diet.
To diagnose this condition, the cholesterol level in the blood should be measured at regular intervals. When a high cholesterol level is detected, it is helpful to be careful in consuming foods that are considered risky.
However, it is not reasonable for a healthy individual to exclude all animal foods from their diet because of fear of cholesterol. However, a healthy individual should not overeat any food anyway.
Here’s an article that might interest you;
Lipids; Fatty Acids, Fats and Oils




Be First to Comment